Introduction: As the popularity and acceptance of cannabis-related products continue to rise, the terms “hemp” and “cannabis” are often used interchangeably, leading to confusion. In this informative article, we’ll delve into the distinctions between hemp and cannabis, exploring their unique characteristics, uses, and the legal implications that set them apart.
Defining Hemp and Cannabis:
- Hemp:
- Botanical Classification: Hemp belongs to the Cannabis sativa plant family.
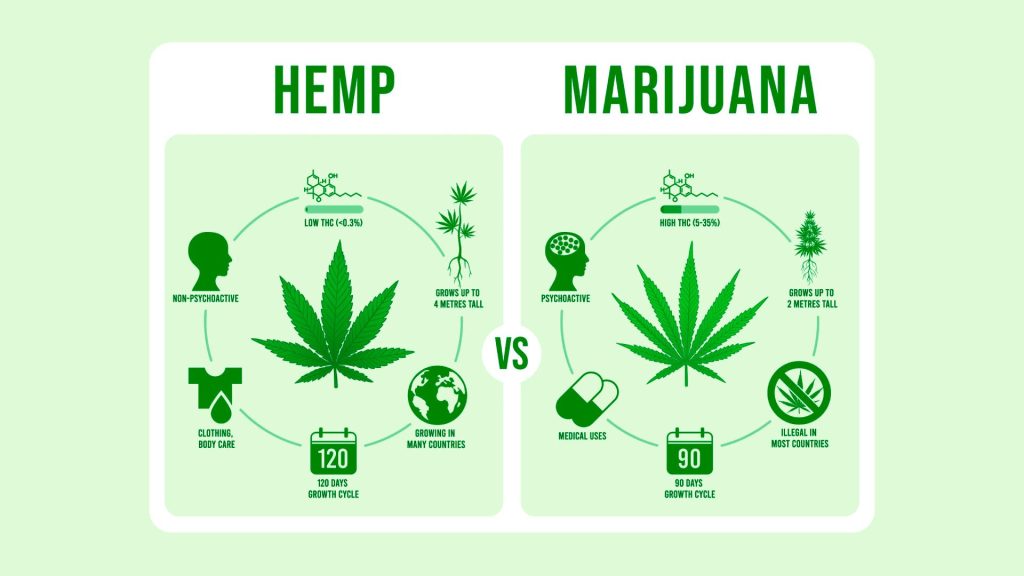
- THC Content: Legally, hemp must contain no more than 0.3% THC (tetrahydrocannabinol), the psychoactive compound responsible for the “high” associated with cannabis.
- Uses: Hemp is cultivated for its versatile fibers, seeds, and extracts. Common applications include textiles, paper, rope, food products, and CBD (cannabidiol) extraction.
- Cannabis:
- Botanical Classification: Cannabis also belongs to the Cannabis sativa plant family.
- THC Content: Cannabis varieties can contain varying levels of THC, often much higher than the 0.3% threshold found in hemp. This is what distinguishes cannabis as a psychoactive substance.
- Uses: Cannabis is primarily grown for medicinal or recreational purposes, as its flowers contain higher levels of THC and other cannabinoids. It is utilized for products such as marijuana, THC concentrates, and medical cannabis.
Key Differences:
- THC Content:
- Hemp has minimal THC content, making it non-intoxicating and suitable for a range of industrial and health-related applications.
- Cannabis contains higher THC levels, leading to psychoactive effects when consumed.
- Cultivation Practices:
- Hemp is often grown in dense fields to maximize fiber and seed production, requiring minimal care compared to high-THC cannabis plants.
- Cannabis cultivation requires more precise conditions, often in controlled environments, to optimize cannabinoid and terpene profiles.
- Legal Status:
- Hemp, with its low THC content, is legal in many countries and widely accepted for industrial and commercial purposes.
- Cannabis regulations vary globally, with some regions allowing medicinal and/or recreational use, while others maintain strict prohibitions.
The Versatility of Hemp: Hemp’s versatility extends beyond its non-intoxicating nature. This resilient plant offers sustainable solutions in various industries, from textiles and construction to nutrition and wellness. The rising popularity of CBD products, derived from hemp, further underscores its potential in the health and wellness sector.
Conclusion: In the ongoing discourse surrounding cannabis, understanding the nuanced differences between hemp and cannabis is crucial. While both belong to the same plant family, their varying THC content, cultivation practices, and uses set them apart. Whether you’re exploring the therapeutic benefits of CBD or the recreational aspects of cannabis, a clear understanding of hemp vs. cannabis paves the way for informed decisions in this rapidly evolving green frontier.
Writien by Ahsan Habib
Here’s more

Navigating the Culinary High: An Edible Dosing Guide for a Positive First-Time Experience
Introduction: Edibles offer a unique and flavorful way to experience the effects of cannabis, but achieving the perfect dose for
Navigating the Endocannabinoid System: Understanding Cannabinoids and Their Interaction with the Body
Introduction: Cannabinoids, the chemical compounds found in cannabis, have gained significant attention for their potential therapeutic effects and their interaction

Rollin’ Right: A Step-by-Step Guide on How to Roll a Joint
Introduction: Rolling a joint is considered an art form among cannabis enthusiasts, and mastering this skill can enhance your overall
Hemp vs. Cannabis – What’s the Difference?
Introduction: As the popularity and acceptance of cannabis-related products continue to rise, the terms “hemp” and “cannabis” are often used

Elevating Your Experience: A Deep Dive into Live Resin Cannabis Concentrates
Introduction: In the ever-evolving world of cannabis concentrates, live resin has emerged as a connoisseur’s delight, offering a potent and

Unveiling the Aromatic Symphony: A Comprehensive Guide to Cannabis Terpenes
Introduction: In the vibrant world of cannabis, terpenes play a crucial role, contributing not only to the plant’s distinctive aroma


